Blepharitis is a common eye condition characterised by inflammation of the eyelids. Symptoms can include redness, itching, crusting near the eyelashes, burning and dryness or, can be present with no symptoms at all. Its presence can affect people of all ages and affects not only the health of the eyelid but the eye itself.
Blepharitis is broadly categorised into two types based on the part of the eyelid affected: anterior blepharitis and posterior blepharitis (also known as MGD- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction) . While these sub-types usually co-exist, they have distinct characteristics, symptoms and treatments which we look into further detail below.

Main Symptoms: crusting, redness of lid margins, itching. Usually worse in the morning.
Causes:
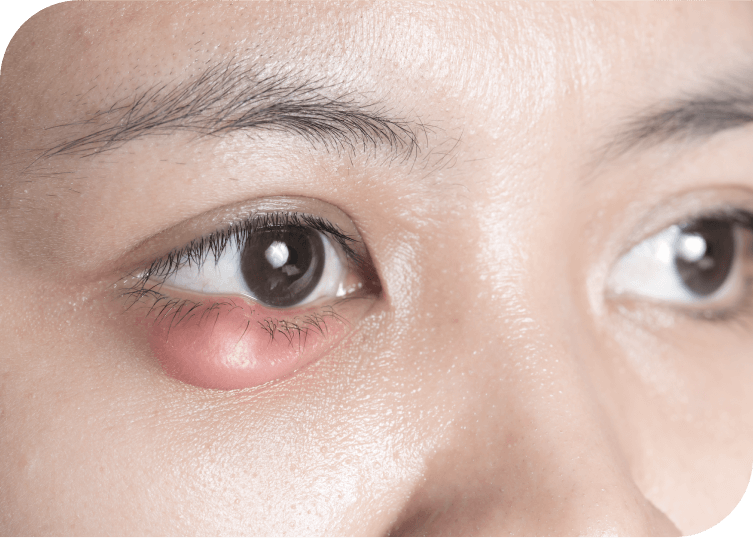
While anterior blepharitis affects the outer eyelid, it can be connected to posterior blepharitis (MGD), which affects the deeper layers and glands within the eyelids in a few ways:
This connection is critical because Meibomian gland dysfunction directly affects the tear film stability, resulting in dry eye symptoms such as burning, grittiness and red eyes.
In summary, anterior blepharitis is a problematic condition that on its own, however it can influence the posterior portion of the eyelid, where meibomian glands are located. Therefore at Dry Eye Wales we always encourage ensuring the lids are free of anterior blepharitis before delving deeper into MGD treatments to ensure the best possible treatment outcomes.
We will do our best to accommodate your busy schedule.